

















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
Sugarcane World Agriculture - The Sweet Giant of the Fields


The Origins and Global Importance of Sugarcane
Sugarcane, with its scientific name Saccharum officinarum, is not just any ordinary crop. It is a true global giant, ranking as the world's largest crop by production volume.
Native to Southeast Asia, sugarcane has a rich history that dates back thousands of years. Around 8,000 years ago, the people of New Guinea and parts of Southeast Asia started cultivating sugarcane for its sweet juice. From there, it spread to India and China, and eventually found its way to the Arabian Peninsula through trade routes.
It was in the Middle Ages that sugarcane made its way to Europe. Christopher Columbus introduced sugar to the New World during his voyages, and it quickly became a common crop in countries like Brazil and the Caribbean, where the climate and soil conditions were ideal for its cultivation.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 4345 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 416 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Sugarcane Cultivation and Production
Today, sugarcane is grown in more than 90 countries around the world, predominantly in tropical and subtropical regions. Brazil is the largest producer, followed by India, China, Thailand, and Pakistan. These countries have vast expanses of land suitable for sugarcane cultivation, as well as favorable climatic conditions.
Successful sugarcane cultivation requires specific conditions. It needs a tropical climate with abundant rainfall and temperatures between 20 and 30 degrees Celsius. The crop thrives in well-drained soils rich in organic matter. It takes about 12 to 18 months for sugarcane to mature and be ready for harvest.
Sugarcane is propagated by planting pieces of mature stalks, known as setts, which take root and grow into new plants. Once planted, the growing cycle of sugarcane begins, and it undergoes several stages before reaching maturity. During this time, farmers must closely monitor the crop, ensuring it receives sufficient water, fertilizer, and protection from pests and diseases.
When the sugarcane is ready for harvest, it is typically cut by hand or with the help of machinery. The stalks are then transported to a sugar mill, where they go through a series of processes to extract the juice. This juice is later refined to produce various sugar products, including granulated sugar, brown sugar, and molasses.
The Versatility of Sugarcane
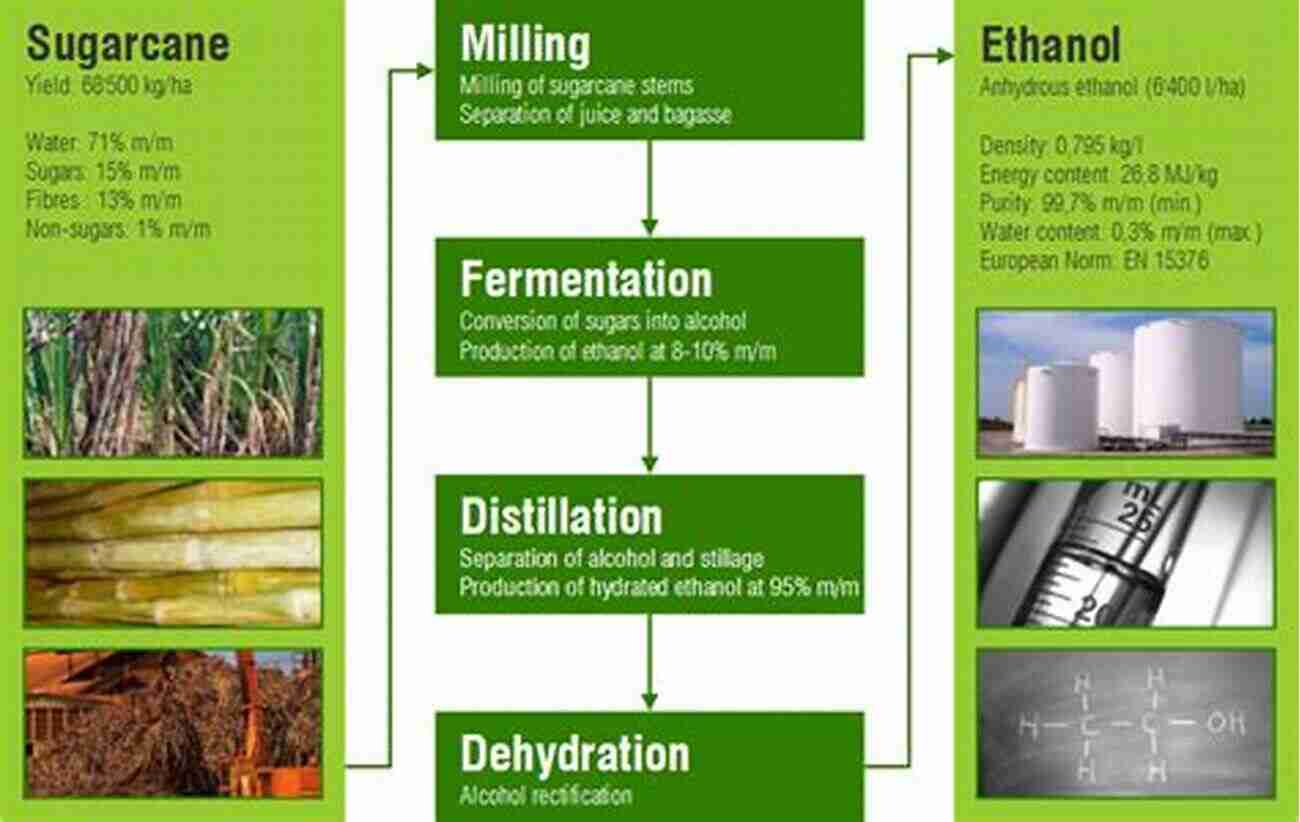
Sugarcane is not only used to satisfy our sweet cravings; it has numerous other applications as well. It serves as a vital raw material in the production of biofuels, particularly ethanol. The ethanol produced from sugarcane is blended with gasoline to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a cleaner environment.
In addition to fuel, sugarcane also plays a role in the production of other useful products such as paper, cardboard, and even certain types of plastics. Its fibrous residue, known as bagasse, is used as a renewable source of energy in biomass power plants, further reducing the reliance on fossil fuels.
The Environmental and Economic Impact
The cultivation of sugarcane not only contributes to the economy but also has several positive environmental impacts. Sugarcane fields act as carbon sinks, absorbing a significant amount of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thereby helping in the fight against climate change.
Furthermore, sugarcane cultivation provides employment opportunities for millions of people worldwide, especially in developing countries. Small-scale farmers often rely on sugarcane as a source of income, allowing them to support their families and invest in their communities.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Like any other crop, sugarcane cultivation faces its fair share of challenges. One of the major concerns is the impact on water resources. Sugarcane is a thirsty crop, requiring a significant amount of water for its growth. Many regions where sugarcane is grown already face water scarcity issues, so balancing water usage becomes crucial.
Another challenge lies in the increasing competition for arable land. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food crops also rises. This puts pressure on the cultivation of sugarcane, as land availability becomes limited.
However, researchers and scientists are always striving to overcome these challenges. Efforts are being made to develop drought-tolerant sugarcane varieties and improve water management practices. Additionally, innovations in farming techniques, such as precision agriculture, hold the promise of optimizing yields while minimizing resource usage.
Sugarcane, with its fascinating history and versatile applications, remains one of the most crucial crops in the world of agriculture. Its contribution to the economy, environment, and energy sector cannot be understated. As we move towards a more sustainable future, sugarcane will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the world agriculture landscape.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 4345 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 416 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
From enhancing the flavour of food to providing a substrate for fermentation, sugar is renowned worldwide for its importance as a commodity. For many centuries sugarcane has been cultivated and developed, and we now have a huge range of crop varieties.
Based on Blackburn's highly successful Sugarcane, originally published in 1984, this new edition has been fully revised and expanded by an international team of widely respected sugarcane specialists. Focussing on the agricultural aspects of the crop, this book follows a logical progression from the botany and breeding through to planning cultivation, control of weeds, pests and diseases, harvest management and payment for cane.
- An invaluable asset to those involved in planning or running sugar estates as well as small producers
- An easy-to-follow reference for students and agriculturalists alike
Comprehensive reference sections and further reading

 Reed Mitchell
Reed MitchellTango For Chromatic Harmonica Dave Brown: Unleashing the...
The hauntingly beautiful sound of the...

 Patrick Rothfuss
Patrick RothfussHow To Tie The 20 Knots You Need To Know
Knot-tying is an essential...

 Vince Hayes
Vince HayesThe Politics Experiences and Legacies of War in the US,...
War has always had a profound impact...

 Leo Mitchell
Leo MitchellThe Psychedelic History Of Mormonism Magic And Drugs
Throughout history, the connections between...

 Michael Simmons
Michael SimmonsThe Practical Japan Travel Guide: All You Need To Know...
Japan, known for its unique...

 Deion Simmons
Deion SimmonsDigital Subtraction Flash Cards in Color: Shuffled Twice...
Mathematics is an essential...

 Emanuel Bell
Emanuel BellUnveiling the Enigma: Explore the Fascinating World of...
Hello, dear readers! Today, we have a...

 Darren Nelson
Darren NelsonHow To Handle Your Parents - A Comprehensive Guide
Are you having trouble dealing with your...

 Jimmy Butler
Jimmy ButlerThe Loopy Coop Hens Letting Go: A Tale of Friendship and...
Once upon a time, in a peaceful...

 Charles Dickens
Charles DickensGreen Are My Mountains: An Autobiography That Will Leave...
Are you ready to embark on an...

 Drew Bell
Drew BellRogue Trainer Secrets To Transforming The Body...
In this fast-paced...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 August HayesThe Legendary HMS Warrior and the Royal Navy Black Battlefleet New Vanguard...
August HayesThe Legendary HMS Warrior and the Royal Navy Black Battlefleet New Vanguard...
 Oliver FosterExperience the Irresistible Delicacy of Yummy Pastry For Meals - Unleash Your...
Oliver FosterExperience the Irresistible Delicacy of Yummy Pastry For Meals - Unleash Your...
 Spencer PowellPeaceful Coexistence: The Wiley Science Editions 79 Curriculum for Making the...
Spencer PowellPeaceful Coexistence: The Wiley Science Editions 79 Curriculum for Making the... Miguel de CervantesFollow ·2.2k
Miguel de CervantesFollow ·2.2k Jay SimmonsFollow ·5.7k
Jay SimmonsFollow ·5.7k Everett BellFollow ·9.9k
Everett BellFollow ·9.9k Pablo NerudaFollow ·6.9k
Pablo NerudaFollow ·6.9k George HayesFollow ·14.6k
George HayesFollow ·14.6k Stan WardFollow ·13.7k
Stan WardFollow ·13.7k Xavier BellFollow ·15.2k
Xavier BellFollow ·15.2k Hamilton BellFollow ·13.2k
Hamilton BellFollow ·13.2k

















