















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
Why are atoms attracted to each other? Unveiling the Secrets of Intermolecular Forces

Have you ever wondered why water molecules stick together, or why certain substances are liquid at room temperature and others are not? The answers lie within the fascinating world of intermolecular forces, the invisible interactions that hold particles together and contribute to the properties of matter. In this article, we will delve deep into the theory of intermolecular forces, uncovering the mechanisms behind this captivating phenomenon.
The Basics: What are Intermolecular Forces?
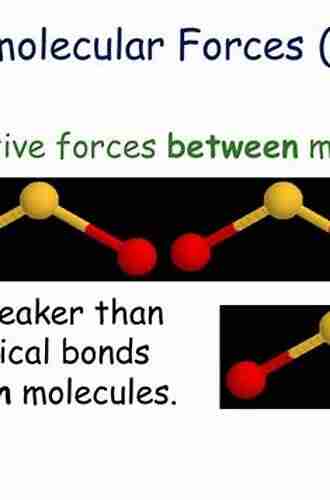
Intermolecular forces refer to the attractive or repulsive interactions that occur between molecules or atoms. These forces determine many physical and chemical properties of substances, such as boiling and melting points, viscosity, and solubility. Understanding intermolecular forces is essential to comprehend the behavior of matter in various states.
Types of Intermolecular Forces
There are four main types of intermolecular forces:
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6690 KB |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 352 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
- London Dispersion Forces: Also known as Van der Waals forces, these are the weakest type of intermolecular forces. They occur between all molecules and are caused by temporary shifts in electron density, which result in temporary dipoles attracting other molecules.
- Dipole-Dipole Forces: These forces exist between polar molecules, where the positive end of one molecule attracts the negative end of another. The strength of this force depends on the difference in electronegativity and the dipole moment of the molecules involved.
- Hydrogen Bonding: A special type of dipole-dipole interaction, hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom (such as nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine) interacts with nearby atoms or molecules. Hydrogen bonding is responsible for the unique properties of water and plays a crucial role in biological systems.
- Ion-Dipole Forces: These forces arise when ions interact with polar molecules. The positive or negative charge of an ion attracts the opposite charge of the polar molecule, resulting in an attractive force between them.
The Impacts of Intermolecular Forces
The strength and type of intermolecular forces directly impact the behavior and properties of substances. Here are some notable effects:
- Boiling and Melting Points: Substances with stronger intermolecular forces generally have higher boiling and melting points. This is because more energy is required to overcome the attractive forces between molecules and transition from one state to another.
- Viscosity: Intermolecular forces also influence a substance's resistance to flow. High viscosity is often observed in substances with strong intermolecular forces, where molecules have greater cohesion and move less freely.
- Solubility: The compatibility of substances in a solution is governed by their intermolecular forces. Polar substances tend to dissolve in polar solvents due to dipole-dipole interactions, while nonpolar substances dissolve in nonpolar solvents, driven by London dispersion forces.
- Surface Tension: Intermolecular forces are responsible for the "skin" on a liquid's surface. They create a cohesive force that holds molecules together, giving rise to phenomena such as capillary action.
- Evaporation and Condensation: The strength of intermolecular forces affects the rate of evaporation and condensation. Substances with weaker forces evaporate more quickly, while those with stronger forces condense at lower temperatures.
The Role of Intermolecular Forces in Everyday Life
Intermolecular forces are all around us, shaping our experiences with matter. Here are some examples of their roles in our daily lives:
- Water's Unique Properties: The hydrogen bonding between water molecules gives it its high boiling point, surface tension, and ability to dissolve many substances. It is also responsible for water's exceptional ability to regulate temperature, making it vital for life as we know it.
- Food and Cooking: Understanding intermolecular forces helps us understand cooking processes. For example, when heating butter, the intermolecular forces holding the solid fat together weaken, resulting in a transition to a liquid state.
- Pharmaceuticals: The effectiveness of drugs depends on their ability to interact with target molecules in the human body. Intermolecular forces play a crucial role in drug-receptor interactions and drug delivery mechanisms.
- Material Sciences: Engineering new materials with desired properties relies on manipulating intermolecular forces. From plastic manufacturing to creating lightweight yet durable metals, the understanding of intermolecular forces paves the way for innovative advancements.
Applications in Future Technologies
Intermolecular forces continue to be a significant area of research, as they offer essential insights for developing new technologies. Here are a few promising applications being explored:
- Nanotechnology: Intermolecular forces are fundamental to understanding the behavior of nanomaterials. By manipulating these forces, scientists can design novel materials with specific properties for use in electronics, medicine, and energy storage.
- Drug Design: Understanding intermolecular forces aids in the development of new drugs with improved efficacy and fewer side effects. By studying how drugs interact with molecular targets, scientists can refine drug molecules for better pharmacological outcomes.
- Green Energy: Developing sustainable energy solutions relies on identifying materials that can efficiently convert solar energy into electrical energy. Intermolecular forces play a critical role in determining the absorption and conversion efficiency of these materials.
The theory of intermolecular forces unravels the hidden attractions that determine the behavior of matter. From the simple to the complex, these forces shape the properties of materials around us and hold the key to future innovations in various fields. By delving into the theory and understanding how these forces manifest, scientists and engineers can unlock new opportunities and develop groundbreaking technologies that propel us into a brighter future.
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6690 KB |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 352 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
The theory of intermolecular forces has advanced very greatly in recent years. It has become possible to carry out accurate calculations of intermolecular forces for molecules of useful size, and to apply the results to important practical applications such as understanding protein structure and function, and predicting the structures of molecular crystals. The Theory of Intermolecular Forces sets out the mathematical techniques that are needed to describe
and calculate intermolecular interactions and to handle the more elaborate mathematical models. It describes the methods that are used to calculate them, including recent developments in the use of density functional theory and symmetry-adapted perturbation theory. The use of higher-rank multipole moments to
describe electrostatic interactions is explained in both Cartesian and spherical tensor formalism, and methods that avoid the multipole expansion are also discussed. Modern ab initio perturbation theory methods for the calculation of intermolecular interactions are discussed in detail, and methods for calculating properties of molecular clusters and condensed matter for comparison with experiment are surveyed.

 Reed Mitchell
Reed MitchellTango For Chromatic Harmonica Dave Brown: Unleashing the...
The hauntingly beautiful sound of the...

 Patrick Rothfuss
Patrick RothfussHow To Tie The 20 Knots You Need To Know
Knot-tying is an essential...

 Vince Hayes
Vince HayesThe Politics Experiences and Legacies of War in the US,...
War has always had a profound impact...

 Leo Mitchell
Leo MitchellThe Psychedelic History Of Mormonism Magic And Drugs
Throughout history, the connections between...

 Michael Simmons
Michael SimmonsThe Practical Japan Travel Guide: All You Need To Know...
Japan, known for its unique...

 Deion Simmons
Deion SimmonsDigital Subtraction Flash Cards in Color: Shuffled Twice...
Mathematics is an essential...

 Emanuel Bell
Emanuel BellUnveiling the Enigma: Explore the Fascinating World of...
Hello, dear readers! Today, we have a...

 Darren Nelson
Darren NelsonHow To Handle Your Parents - A Comprehensive Guide
Are you having trouble dealing with your...

 Jimmy Butler
Jimmy ButlerThe Loopy Coop Hens Letting Go: A Tale of Friendship and...
Once upon a time, in a peaceful...

 Charles Dickens
Charles DickensGreen Are My Mountains: An Autobiography That Will Leave...
Are you ready to embark on an...

 Drew Bell
Drew BellRogue Trainer Secrets To Transforming The Body...
In this fast-paced...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Garrett PowellAcing the Clep Information Systems Exam: Your Ultimate Guide to Success |...
Garrett PowellAcing the Clep Information Systems Exam: Your Ultimate Guide to Success |...
 Percy Bysshe ShelleyKey Influences On Buying Selling Market Growth Technology Management Business
Percy Bysshe ShelleyKey Influences On Buying Selling Market Growth Technology Management Business Jarrett BlairFollow ·14.4k
Jarrett BlairFollow ·14.4k Willie BlairFollow ·12.4k
Willie BlairFollow ·12.4k Mike HayesFollow ·9.2k
Mike HayesFollow ·9.2k Clay PowellFollow ·4.2k
Clay PowellFollow ·4.2k Jean BlairFollow ·11.3k
Jean BlairFollow ·11.3k Jack ButlerFollow ·16k
Jack ButlerFollow ·16k Evan HayesFollow ·13.4k
Evan HayesFollow ·13.4k Angelo WardFollow ·7k
Angelo WardFollow ·7k