

















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
The Philosophy Of The Enlightenment Updated Edition: Unveiling the Secrets of an Intellectual Revolution


Have you ever wondered about the origins of modern democratic societies, the concept of individual rights, or the pursuit of knowledge through reason? Look no further! This comprehensive and updated edition delves into the profound philosophy of the Enlightenment, a period of intellectual revolution that shaped the world we live in today.
The Enlightenment: A Brief Overview
The Enlightenment, also known as the Age of Reason, was an intellectual movement that emerged in Europe during the 17th and 18th centuries. It brought about a radical change in the way people perceived the world, shifting the focus from religious authority to reason and individualism. This period witnessed a surge in scientific discovery, skepticism towards traditional beliefs, and a desire to challenge political and social norms.
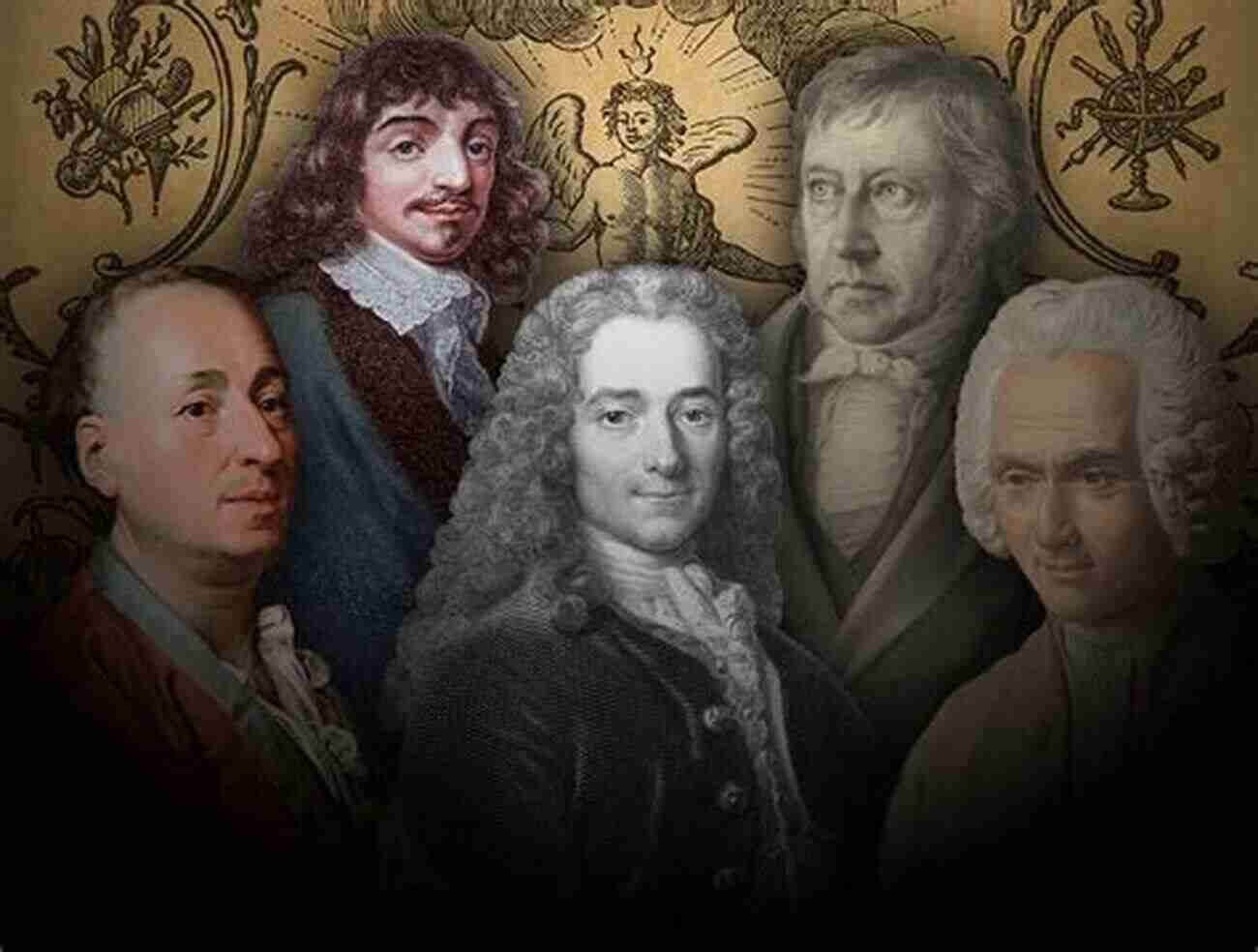

Key Thinkers and Ideas
The core principles of the Enlightenment were based on reason, science, and humanism. Prominent thinkers such as Voltaire, Rousseau, Locke, and Montesquieu championed these ideals through their writings and activism.
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 39252 KB |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 392 pages |
| X-Ray | : | Enabled |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
Voltaire: The Advocate of Freedom
Voltaire, a French philosopher and writer, championed the principles of free speech, religious tolerance, and the separation of church and state. His witty and satirical works, including the famous novella Candide, criticized the oppressive aristocracy and the Catholic Church. Voltaire's ideas greatly influenced the shaping of modern liberal democracies.
Rousseau: The Social Contract
Jean-Jacques Rousseau's influential work The Social Contract argued that individuals should surrender some of their freedoms to the general will of society in order to ensure the common good. This idea formed the basis of modern social contract theory, which emphasizes the importance of collective decision-making and governmental consent.
Locke: Natural Rights and Limited Government
John Locke, an English philosopher, put forward the concept of natural rights – the belief that individuals possess inherent rights to life, liberty, and property. His political ideas greatly influenced the American Revolution and the drafting of the United States Constitution. Locke believed in the necessity of a limited government that protects these rights and represents the will of the people.

The Legacy of the Enlightenment
The ideas of the Enlightenment continue to shape our modern world. This intellectual movement has had a profound impact on politics, science, and culture.
Revolutionizing Politics and Government
The Enlightenment laid the foundation for modern democratic societies and inspired revolutions such as the American Revolution and the French Revolution. It promoted the ideas of individual rights, equality, and popular sovereignty, challenging the traditional authority of monarchies and paving the way for representative governments.
Advancing Scientific Knowledge
The Enlightenment also marked a turning point in scientific exploration and discovery. Thinkers like Isaac Newton and Francis Bacon brought about a scientific revolution that embraced empirical evidence and rational thinking. This emphasis on the scientific method led to breakthroughs in various fields, including physics, astronomy, and medicine.
Transforming Culture and Art
Enlightenment ideas found expression not only in intellectual debates and political movements but also in art, literature, and music. The movement encouraged the questioning of traditional norms and values, promoting individual expression and creativity. This gave rise to literary works and artistic movements that celebrated human emotions, reason, and the power of imagination.

The Importance of Understanding the Enlightenment
Studying the Enlightenment is crucial for comprehending the foundations of our modern world. By exploring the ideas and philosophies of this era, we gain insights into the origins of democracy, the importance of reason, and the ongoing struggle for human rights.
As we face contemporary challenges and navigate the complexities of the 21st century, the Enlightenment serves as a reminder that progress and change can be achieved through critical thinking, intellectual discourse, and a commitment to liberty and equality.
The Philosophy of the Enlightenment Updated Edition is your key to uncovering the intellectual revolution that shaped the world. By delving into the ideas of Enlightenment thinkers, you will gain a deeper understanding of the origins of modern democracy, individual rights, and the pursuit of knowledge through reason.
Embrace the Enlightenment’s legacy, and embark on a journey of intellectual exploration that will enrich your perception of history and the world around you.
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 39252 KB |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 392 pages |
| X-Ray | : | Enabled |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
In this classic work of intellectual history, Ernst Cassirer provides both a cogent synthesis and a penetrating analysis of one of history's greatest intellectual epochs: the Enlightenment. Arguing that there was a common foundation beneath the diverse strands of thought of this period, he shows how Enlightenment philosophers drew upon the ideas of the preceding centuries even while radically transforming them to fit the modern world. In Cassirer's view, the Enlightenment liberated philosophy from the realm of pure thought and restored it to its true place as an active and creative force through which knowledge of the world is achieved.
In a new foreword, Peter Gay considers The Philosophy of the Enlightenment in the context in which it was written--Germany in 1932, on the precipice of the Nazi seizure of power and one of the greatest assaults on the ideals of the Enlightenment. He also argues that Cassirer's work remains a trenchant defense against enemies of the Enlightenment in the twenty-first century.

 Reed Mitchell
Reed MitchellTango For Chromatic Harmonica Dave Brown: Unleashing the...
The hauntingly beautiful sound of the...

 Patrick Rothfuss
Patrick RothfussHow To Tie The 20 Knots You Need To Know
Knot-tying is an essential...

 Vince Hayes
Vince HayesThe Politics Experiences and Legacies of War in the US,...
War has always had a profound impact...

 Leo Mitchell
Leo MitchellThe Psychedelic History Of Mormonism Magic And Drugs
Throughout history, the connections between...

 Michael Simmons
Michael SimmonsThe Practical Japan Travel Guide: All You Need To Know...
Japan, known for its unique...

 Deion Simmons
Deion SimmonsDigital Subtraction Flash Cards in Color: Shuffled Twice...
Mathematics is an essential...

 Emanuel Bell
Emanuel BellUnveiling the Enigma: Explore the Fascinating World of...
Hello, dear readers! Today, we have a...

 Darren Nelson
Darren NelsonHow To Handle Your Parents - A Comprehensive Guide
Are you having trouble dealing with your...

 Jimmy Butler
Jimmy ButlerThe Loopy Coop Hens Letting Go: A Tale of Friendship and...
Once upon a time, in a peaceful...

 Charles Dickens
Charles DickensGreen Are My Mountains: An Autobiography That Will Leave...
Are you ready to embark on an...

 Drew Bell
Drew BellRogue Trainer Secrets To Transforming The Body...
In this fast-paced...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Anton Foster5 Energy Efficient Fault Tolerant Systems that Revolutionize Embedded Systems
Anton Foster5 Energy Efficient Fault Tolerant Systems that Revolutionize Embedded Systems
 Kevin TurnerThe Whispers In The Walls Scarlet And Ivy - Unveiling the Secrets of Rookwood...
Kevin TurnerThe Whispers In The Walls Scarlet And Ivy - Unveiling the Secrets of Rookwood... Preston SimmonsFollow ·5.2k
Preston SimmonsFollow ·5.2k Francisco CoxFollow ·9.1k
Francisco CoxFollow ·9.1k Galen PowellFollow ·11k
Galen PowellFollow ·11k Brennan BlairFollow ·7.2k
Brennan BlairFollow ·7.2k Ervin BellFollow ·5k
Ervin BellFollow ·5k Dalton FosterFollow ·9.3k
Dalton FosterFollow ·9.3k Jon ReedFollow ·18.2k
Jon ReedFollow ·18.2k Gavin MitchellFollow ·2.9k
Gavin MitchellFollow ·2.9k




















