














Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
Spin Transfer Torque MRAM and Beyond

Imagine a world where computer memory can be faster, more reliable, and have greater endurance than ever before. This may sound like a distant dream, but thanks to Spin Transfer Torque Magnetic Random-Access Memory (STT-MRAM),this reality is closer than ever. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of STT-MRAM and discuss its potential beyond just computer memory.
The Basics of MRAM
Before we dive deeper into STT-MRAM, it's important to understand the basics of Magnetic Random-Access Memory (MRAM). MRAM is a type of non-volatile memory that uses magnetic elements to store and retrieve data. Unlike traditional forms of memory like Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DRAM) or Flash memory, MRAM retains data even when the power is turned off. This makes it ideal for applications where data integrity is crucial, such as automotive systems, industrial controls, and IoT devices.
Introducing Spin Transfer Torque MRAM
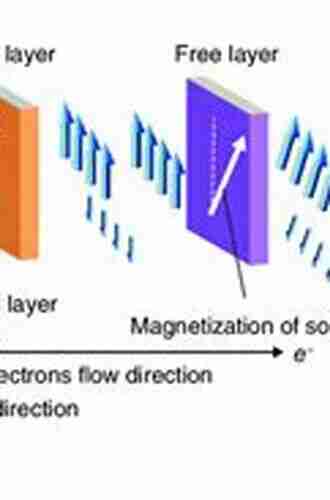
Spin Transfer Torque MRAM (STT-MRAM) is the next evolutionary step in MRAM technology. It utilizes the spin of electrons to store and manipulate data, which brings several advantages over traditional MRAM designs. One of the primary benefits of STT-MRAM is its faster write and read speeds compared to previous MRAM technologies. This is achieved by using spin-polarized currents to switch the magnetic orientation of the storage elements, resulting in faster and more efficient data access.
4.6 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 38521 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 339 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Another advantage of STT-MRAM is its improved endurance. Traditional MRAM technologies suffer from write endurance limitations, meaning they can only handle a finite number of write cycles before degradation occurs. However, STT-MRAM has significantly higher endurance, making it more suitable for applications that require frequent updates and changes in data.
Furthermore, STT-MRAM offers better scalability, meaning it can be fabricated using smaller process nodes, leading to denser memory arrays and increased storage capacity. This scalability, coupled with its non-volatile nature, makes STT-MRAM an ideal candidate for future memory technologies.
Applications and Beyond
So, how does STT-MRAM extend beyond just computer memory? The unique properties of STT-MRAM make it well-suited for a wide range of applications. One notable area is in cache memory within processors. By incorporating STT-MRAM as cache memory, processors can benefit from faster and more efficient data access, leading to improved overall performance.
Another exciting application is in the field of artificial intelligence and machine learning. These domains require vast amounts of memory to handle complex tasks. STT-MRAM's high endurance and scalability make it a potential game-changer in this realm, enabling more efficient and powerful AI systems.
Beyond computing, STT-MRAM also holds promise in fields such as high-speed data communication and storage. Its fast write and read speeds, coupled with low power consumption, can revolutionize data transfer and storage technologies, opening up new possibilities for high-speed data processing and analysis.
As we delve further into the digital age, the demand for faster, more reliable, and scalable memory technologies continues to grow. Spin Transfer Torque MRAM (STT-MRAM) represents a significant advancement in the world of MRAM, offering faster speeds, improved endurance, and better scalability. Beyond just computer memory, STT-MRAM has the potential to impact a wide range of domains, from AI to high-speed data communication. This technology holds great promise for the future of computing and beyond.
4.6 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 38521 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 339 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
STAY UP TO DATE ON THE STATE OF MRAM TECHNOLOGY AND ITS APPLICATIONS WITH THIS COMPREHENSIVE RESOURCE
Magnetic Memory Technology: Spin-Transfer-Torque MRAM and Beyond delivers a combination of foundational and advanced treatments of the subjects necessary for students and professionals to fully understand MRAM and other non-volatile memories, like PCM, and ReRAM. The authors offer readers a thorough to the fundamentals of magnetism and electron spin, as well as a comprehensive analysis of the physics of magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) devices as it relates to memory applications.
This book explores MRAM's unique ability to provide memory without requiring the atoms inside the device to move when switching states. The resulting power savings and reliability are what give MRAM its extraordinary potential. The authors describe the current state of academic research in MRAM technology, which focuses on the reduction of the amount of energy needed to reorient magnetization.
Among other topics, readers will benefit from the book's discussions of:
- An to basic electromagnetism, including the fundamentals of magnetic force and other concepts
- An thorough description of magnetism and magnetic materials, including the classification and properties of magnetic thin film properties and their material preparation and characterization
- A comprehensive description of Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) and tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR) devices and their equivalent electrical model
- Spin current and spin dynamics, including the properties of spin current, the Ordinary Hall Effect, the Anomalous Hall Effect, and the spin Hall effect
- Different categories of magnetic random-access memory, including field-write mode MRAM, Spin-Torque-Transfer (STT) MRAM, Spin-Orbit Torque (SOT) MRAM, and others
Perfect for senior undergraduate and graduate students studying electrical engineering, similar programs, or courses on topics like spintronics, Magnetic Memory Technology: Spin-Transfer-Torque MRAM and Beyond also belongs on the bookshelves of engineers and other professionals involved in the design, development, and manufacture of MRAM technologies.

 Reed Mitchell
Reed MitchellTango For Chromatic Harmonica Dave Brown: Unleashing the...
The hauntingly beautiful sound of the...

 Patrick Rothfuss
Patrick RothfussHow To Tie The 20 Knots You Need To Know
Knot-tying is an essential...

 Vince Hayes
Vince HayesThe Politics Experiences and Legacies of War in the US,...
War has always had a profound impact...

 Leo Mitchell
Leo MitchellThe Psychedelic History Of Mormonism Magic And Drugs
Throughout history, the connections between...

 Michael Simmons
Michael SimmonsThe Practical Japan Travel Guide: All You Need To Know...
Japan, known for its unique...

 Deion Simmons
Deion SimmonsDigital Subtraction Flash Cards in Color: Shuffled Twice...
Mathematics is an essential...

 Emanuel Bell
Emanuel BellUnveiling the Enigma: Explore the Fascinating World of...
Hello, dear readers! Today, we have a...

 Darren Nelson
Darren NelsonHow To Handle Your Parents - A Comprehensive Guide
Are you having trouble dealing with your...

 Jimmy Butler
Jimmy ButlerThe Loopy Coop Hens Letting Go: A Tale of Friendship and...
Once upon a time, in a peaceful...

 Charles Dickens
Charles DickensGreen Are My Mountains: An Autobiography That Will Leave...
Are you ready to embark on an...

 Drew Bell
Drew BellRogue Trainer Secrets To Transforming The Body...
In this fast-paced...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Dalton FosterThe Kid, The Hawk, Rock, Vladi, Pedro, Le Grand Orange, Youppi!: The Crazy...
Dalton FosterThe Kid, The Hawk, Rock, Vladi, Pedro, Le Grand Orange, Youppi!: The Crazy... Dwayne MitchellFollow ·15.2k
Dwayne MitchellFollow ·15.2k Hamilton BellFollow ·13.2k
Hamilton BellFollow ·13.2k Robbie CarterFollow ·5.5k
Robbie CarterFollow ·5.5k Jett PowellFollow ·5.9k
Jett PowellFollow ·5.9k Brady MitchellFollow ·5.2k
Brady MitchellFollow ·5.2k Michael CrichtonFollow ·12k
Michael CrichtonFollow ·12k Mario SimmonsFollow ·14.4k
Mario SimmonsFollow ·14.4k Clark CampbellFollow ·6.6k
Clark CampbellFollow ·6.6k