

















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
Insect Pests of Millets: Systematics, Bionomics, and Management


Do you love millets? These nutritious and versatile grains have been gaining popularity in recent years due to their numerous health benefits. However, just like any other crop, millets are not immune to pest infestations. In this article, we will explore the various insect pests that pose a threat to millets, dive into their systematics and bionomics, and discuss effective management strategies to protect these valuable crops.
The Importance of Millets
Millets have been cultivated for thousands of years and play a crucial role in food security, especially in arid and semi-arid regions. Their ability to thrive in challenging environments with minimal water and nutrient requirements makes them an excellent choice for sustainable agriculture. Furthermore, millets are gluten-free, rich in nutrients, and exhibit low glycemic index, making them ideal for individuals with specific dietary needs.
An Overview of Insect Pests
Insects are the most significant group of pests affecting millets worldwide. The damage caused by these pests can result in significant yield losses if left unmanaged. It is essential for farmers, researchers, and agricultural enthusiasts to have a comprehensive understanding of the various insect pests that target millets and their life cycles.
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 105591 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 191 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Hardcover | : | 258 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 2.65 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.14 x 0.63 x 9.21 inches |
Systematics of Insect Pests of Millets
The systematic classification of insect pests of millets provides insights into their evolutionary relationships and helps in identifying similarities and patterns among different species. By understanding the systematics, we can better predict the behavior, adaptability, and potential threats posed by these pests.
Bionomics of Insect Pests of Millets
Bionomics refers to the study of the biological characteristics and interactions of organisms within their environments. In the context of insect pests of millets, studying their bionomics helps us uncover crucial information about their feeding habits, reproduction patterns, preferred habitats, and vulnerability to natural and artificial control measures.
Major Insect Pests of Millets
In this section, we will delve into the most commonly encountered insect pests of millets and provide detailed descriptions that will assist you in identifying them:
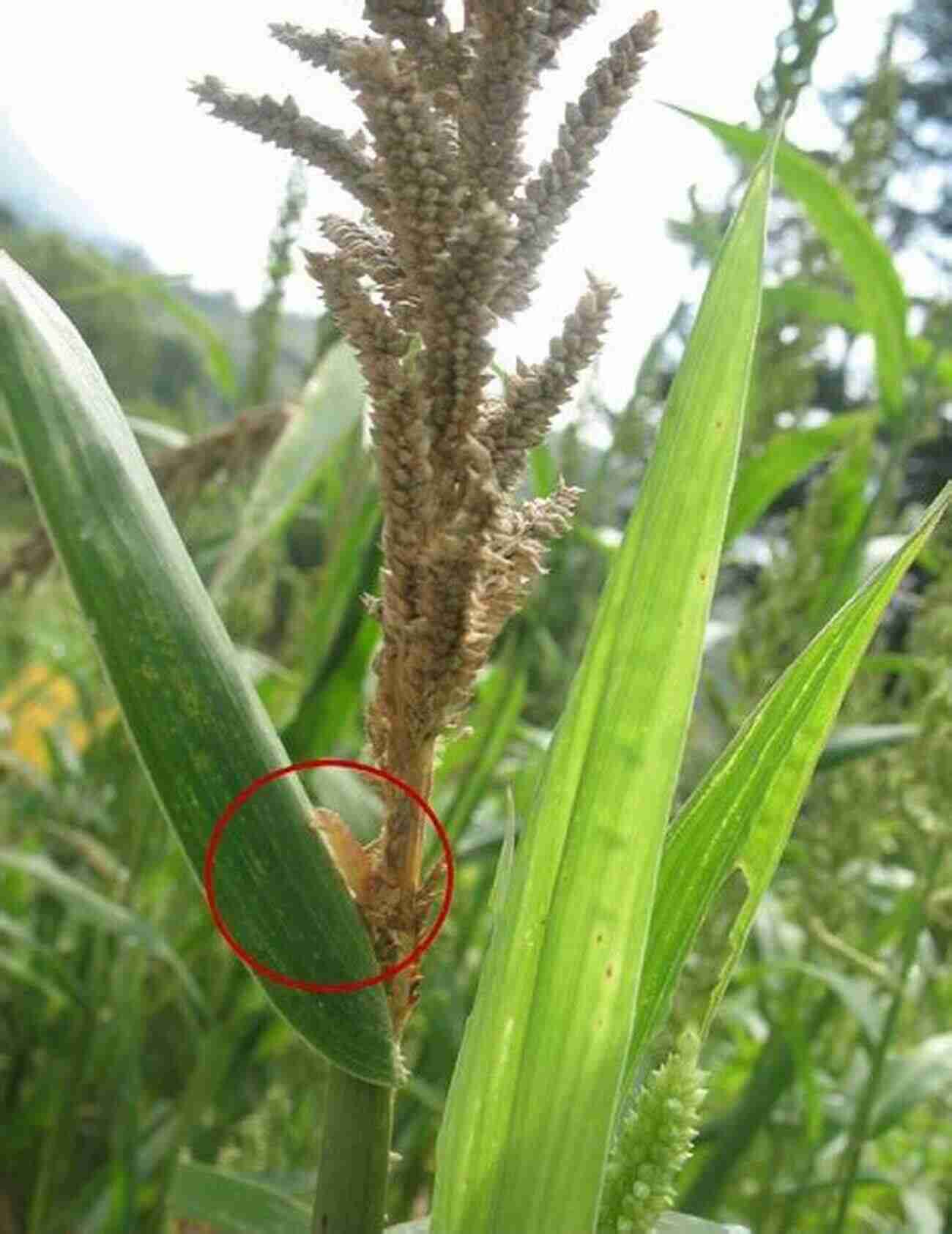
1. Millet Head Miner (Heliocheilus spp.)
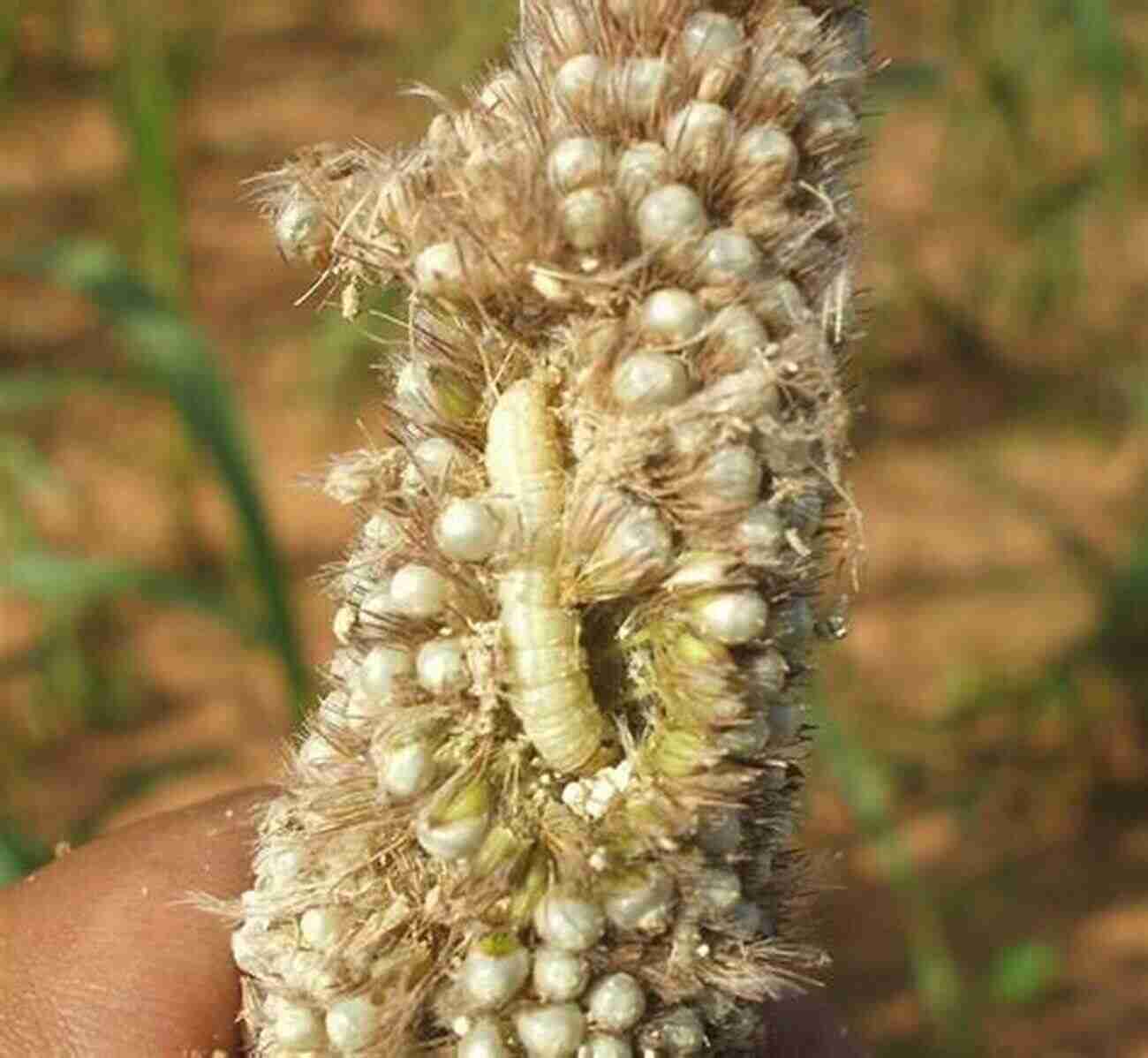

The Millet Head Miner is a notorious pest that damages the reproductive structures of millets, such as the flowering heads and young grains. It typically infests pearl millet and finger millet crops, leading to significant yield losses. Its life cycle, feeding behavior, and preferred ground conditions make it a challenging pest to control.
2. Stem Borers (Conogethes spp., Chilo spp., and Sesamia spp.)

Stem borers are a group of insects that tunnel into the stems of millet plants, causing weakening and drying out of the affected stems. They feed on the internal tissues, which hampers the transportation of water and nutrients, ultimately leading to stunted growth and reduced grain production.
3. Shoot Fly (Atherigona spp.)

The Shoot Fly attacks young millet plants by laying eggs near the base of the stems. Upon hatching, the larvae feed on the tender shoots, disrupting the plant's growth and development. Shoot Fly infestations can result in severe yield losses, affecting both grain quality and quantity.
4. Stored Grain Pests (Sitophilus spp., Rhyzopertha spp., and Tribolium spp.)

Stored grain pests are insects that infest millet grains during storage. These pests can cause considerable damage, leading to reduced germination rates, mold growth, and contamination. Preventive measures and proper storage techniques are vital in minimizing the risk of stored grain infestations.
Effective Pest Management Strategies
Given the potential economic impact of insect pests on millets, implementing effective management strategies is crucial. Here are some practices that can help in mitigating pest damage:
1. Crop Rotation
Rotating millet crops with non-host plants can disrupt the life cycle of many insect pests, reducing their populations and minimizing damage. Incorporating leguminous crops into the rotation can also enhance soil fertility and provide natural pest control benefits through nitrogen fixation.
2. Biological Control
The use of beneficial insects, such as predators, parasitoids, and pathogens, can significantly contribute to pest management. Introducing natural enemies of insect pests can help maintain ecological balance in millet fields and reduce reliance on synthetic pesticides.
3. Cultural Practices
Implementing cultural practices like timely sowing, removal of crop residues, and proper weed control can create unfavorable conditions for insect pests. By depriving pests of their preferred habitats and food sources, their population growth can be limited.
4. Chemical Control
When necessary, judicious use of pesticides can be considered as a part of an integrated pest management approach. However, careful attention must be given to proper timing, dosage, and selection of pesticides to minimize ecological impact and prevent the development of insecticide resistance.
Millets are an essential crop that faces several challenges due to insect pests. Understanding the systematics and bionomics of these pests is crucial in developing effective management strategies. By implementing integrated pest management techniques and adopting sustainable agricultural practices, we can ensure the long-term success and productivity of millet crops while minimizing the reliance on synthetic pesticides. Together, we can protect and promote the growth of this nutritious grain for future generations.
4.4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 105591 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 191 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Hardcover | : | 258 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 2.65 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.14 x 0.63 x 9.21 inches |
Insect Pests of Millets: Systematics, Bionomics, and Management focuses on protecting the cultivated cereals that many worldwide populations depend on for food across the semi-arid tropics of the world. Providing coverage of all the major cultivated millets, including sorghum, pearlmillet, finger millet, barnyard millet, prosomillet, little millet, kodomillet, and foxtail millet, this comprehensive book on insect pests is the first of its kind that explores systematics, bionomics, distribution, damage, host range, biology, monitoring techniques, and management options, all accompanied by useful illustrations and color plates.
By exploring the novel aspects of Insect-plant relationships, including host signaling orientation, host specialization, pest – host evolutionary relationship, and biogeography of insects and host plants, the book presents the latest ecologically sound and innovative techniques in insect pest management from a general overview of pest management to new biotechnological interventions.
- Includes the most comprehensive and relevant aspects of insect systematics, including synonyms, nomenclatural history, and identification characters to quickly guide readers to desired information
- Addresses aspects of insect-plant relationships, including host signaling and orientation, host specialization, pest – host evolutionary relationship, and biogeography of insects and host plant
- Presents the latest research findings related to the ecological, behavioral, and physiological aspects of millet pests

 Reed Mitchell
Reed MitchellTango For Chromatic Harmonica Dave Brown: Unleashing the...
The hauntingly beautiful sound of the...

 Patrick Rothfuss
Patrick RothfussHow To Tie The 20 Knots You Need To Know
Knot-tying is an essential...

 Vince Hayes
Vince HayesThe Politics Experiences and Legacies of War in the US,...
War has always had a profound impact...

 Leo Mitchell
Leo MitchellThe Psychedelic History Of Mormonism Magic And Drugs
Throughout history, the connections between...

 Michael Simmons
Michael SimmonsThe Practical Japan Travel Guide: All You Need To Know...
Japan, known for its unique...

 Deion Simmons
Deion SimmonsDigital Subtraction Flash Cards in Color: Shuffled Twice...
Mathematics is an essential...

 Emanuel Bell
Emanuel BellUnveiling the Enigma: Explore the Fascinating World of...
Hello, dear readers! Today, we have a...

 Darren Nelson
Darren NelsonHow To Handle Your Parents - A Comprehensive Guide
Are you having trouble dealing with your...

 Jimmy Butler
Jimmy ButlerThe Loopy Coop Hens Letting Go: A Tale of Friendship and...
Once upon a time, in a peaceful...

 Charles Dickens
Charles DickensGreen Are My Mountains: An Autobiography That Will Leave...
Are you ready to embark on an...

 Drew Bell
Drew BellRogue Trainer Secrets To Transforming The Body...
In this fast-paced...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Dylan HayesExperiments In Reduced Gravity Sediment Settling On Mars: Unveiling Insights...
Dylan HayesExperiments In Reduced Gravity Sediment Settling On Mars: Unveiling Insights...
 Angelo WardThe Enchanting World of Belladonna Adalyn Grace: Unveiling the Extraordinary...
Angelo WardThe Enchanting World of Belladonna Adalyn Grace: Unveiling the Extraordinary...
 Branson CarterThe Thrilling Native Bones Zeb Hanks Mystery: Uncovering the Secrets That Lie...
Branson CarterThe Thrilling Native Bones Zeb Hanks Mystery: Uncovering the Secrets That Lie... Dashawn HayesFollow ·8.5k
Dashawn HayesFollow ·8.5k Melvin BlairFollow ·15.5k
Melvin BlairFollow ·15.5k Jamal BlairFollow ·6.5k
Jamal BlairFollow ·6.5k Ed CooperFollow ·7.7k
Ed CooperFollow ·7.7k Stanley BellFollow ·16.6k
Stanley BellFollow ·16.6k Anton FosterFollow ·11.2k
Anton FosterFollow ·11.2k Ralph Waldo EmersonFollow ·10.9k
Ralph Waldo EmersonFollow ·10.9k Henry David ThoreauFollow ·11.9k
Henry David ThoreauFollow ·11.9k


















